05_Netty_NIO与零拷贝
基本介绍
所谓零拷贝,不是不拷贝,而是没有CPU 拷贝;
- 零拷贝是网络编程的关键,很多性能优化都离不开零拷贝;
- 在Java程序中,常用的零拷贝有mmap(内存映射)和sendFile。那么,他们在OS里,到底是怎么样的一个设计?我们分析mmap和sendFile这两个零拷贝;
- NIO中又是如何使用零拷贝;
传统IO数据读写
Java传统IO和网络编程的一段代码:
File file = new File("test.txt");
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw");
byte[] arr = new byte[(int)file.length()];
raf.read(arr);
Socket socket = new ServerSocket(8080).accept();
socket.getOutputStream().write(arr);
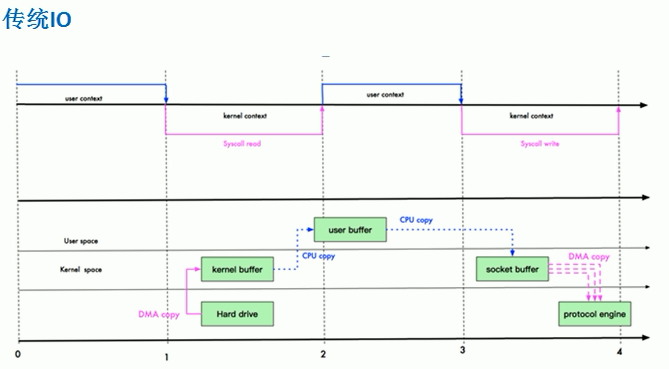
DMA copy:direct memory access,直接内存拷贝,不使用CPU
经过四次拷贝,三次切换
四次拷贝:
- 从硬盘经过DMA拷贝到kernel buffer(内核buffer)
- 从kernel buffer经过cpu拷贝到user buffer,比如拷贝到应用程序
- 从user buffer拷贝到socket buffer
- 从socket buffer拷贝到protocol engine(协议栈)
三次状态切换:
- 用户态->内核状【用户上下文->内核上下文】
- 内核状->用户状
- 用户状->内核状
mmap优化
mmap通过内存映射,将文件映射到内核缓冲区,同时,用户空间可以共享内核空间的数据。这样,在进行网络传输的时候,就可以减少内核空间到用户空间的拷贝次数;
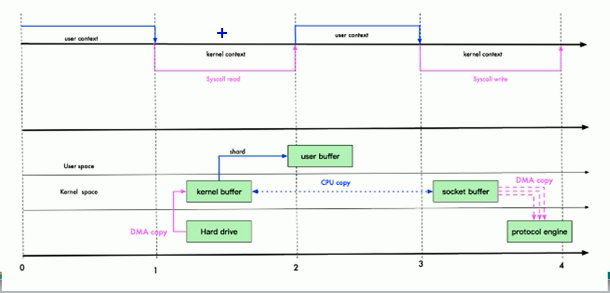
拷贝次数减少为三次,但是状态的切换还是三次;
三次拷贝:
- DMA拷贝,从硬件拷贝到内核空间
- 因为user buffer和kernel buffer共享数据,所以不需要把数据从kernel buffer拷贝到user buffer,数据可以直接在内核空间修改;
- kernel buffer中的数据经过cpu拷贝到socket buffer
- socket buffer经过DMA拷贝到protocol engine
sendFile优化
Linux 2.1版本
Linux2.1版本提供了sendFile函数,其基本原理如下:
数据根本不经过用户态,直接从内核缓冲区进入到SocketBuffer,同时,由于和用户态完全无关,就减少了一次上下文切换;
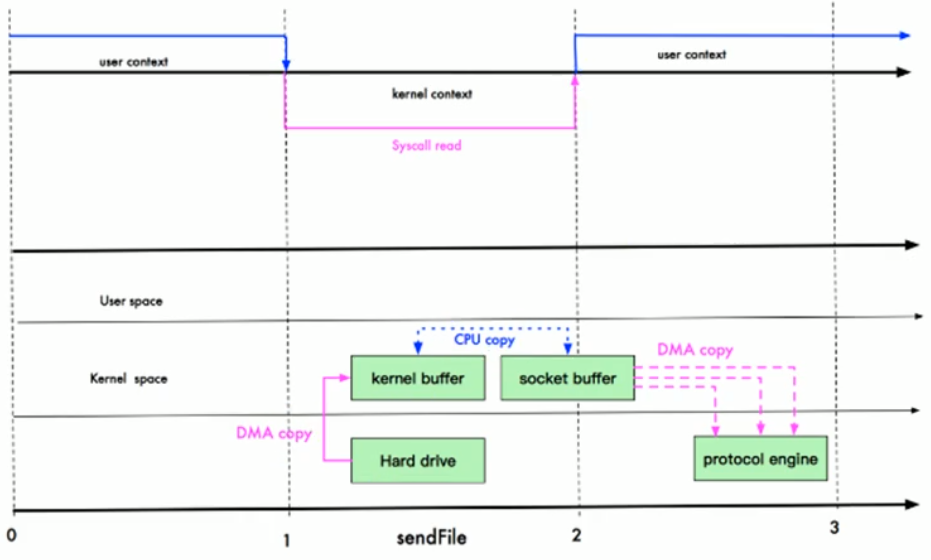
还是三次拷贝,但是减少为两次切换
三次拷贝:
- 从硬件DMA拷贝到kernel buffer
- kernel buffer又经过CPU 拷贝到socket buffer
- socket buffer通过DMA拷贝到protocol engine
Linux 2.4版本
Linux在2.4版本中,做了一些修改,避免了从内核缓冲区拷贝到socket buffer的操作,直接拷贝到协议栈,从而再一次减少了数据拷贝;
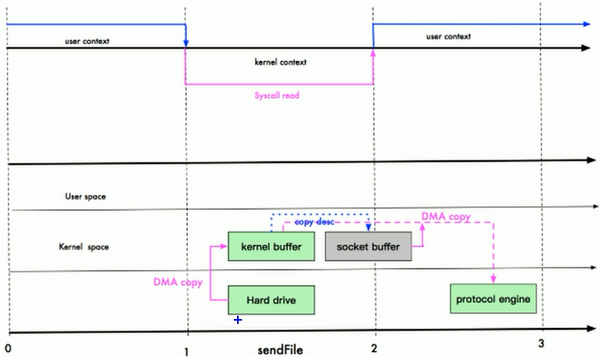
两次拷贝:
- DMA拷贝,将数据从硬件拷贝到kernel buffer
- DMA拷贝,将数据从kernel buffer拷贝到protocol engine
没有经过cpu拷贝,也就是操作系统级别的拷贝,实现了真正的零拷贝;
注意:sendFile技术还是有少量的数据使用了cpu拷贝,如数据的大小(length)、偏移量(offset)等,从kernel buffer拷贝到socket buffer,但是数据量很少,消耗低,可以忽略不计;
零拷贝的再次理解
- 我们所说的零拷贝,是从操作系统的角度来说的。因为内核缓冲之间,没有数据是重复的(只有kernel buffer有一份数据);
- 零拷贝不仅仅带来更少的数据复制,还能带来其他的性能优势,例如更少的上下文切换,更少的CPU缓存伪共享以及无CPU校验和计算;
mmap和sendFile的区别
- mmap适合小数据量的读写,sendFile适合大文件传输;
- mmap需要3次上下文切换,3次数据拷贝;
- sendFile需要2次上下文切换,最少2次数据拷贝;
- sendFile可以利用DMA方式,减少CPU拷贝,mmap则不能(必须从内核拷贝到Socket缓冲区);
NIO 零拷贝实例
案例要求:
- 使用传统的IO方法传递一个大文件;
- 使用NIO零拷贝的方式传递(transferTo)一个大文件;
- 看看两个传递方式耗费时间分别是多少;
传统的零拷贝
服务器端:
public class OldIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7001);
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
try{
byte[] byteArray = new byte[4096];
while (true){
int readCount = dataInputStream.read(byteArray, 0, byteArray.length);
if(-1==readCount){
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端:
public class OldIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 7001);
String fileName = "Xxx.zip";
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
long readCount = 0;
long total = 0;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((readCount = inputStream.read(buffer))>=0){
total += readCount;
dataOutputStream.write(buffer);
}
System.out.println("发送总字节数:"+total+",耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime));
dataOutputStream.close();
socket.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}
transferTo零拷贝
服务器端:
public class NewIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7001);
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket();
serverSocket.bind(inetSocketAddress);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096);
while (true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int readCount = 0;
while (-1!=readCount){
readCount = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
}
// byteBuffer倒带,position=0,mark作废
byteBuffer.rewind();
}
}
}
客户端:
public class NewIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",7001));
String fileName = "Xxx.zip";
// 得到一个文件的Channel
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(fileName).getChannel();
// 准备发送
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 在Linux下一个transferTo方法就可以完成传输
// 在windows下一次调用transferTo只能发送8m,就需要分段传输文件,而且要注意传输时的位置
// transferTo底层就使用了零拷贝
long transferCount = fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
System.out.println("发送的总的字节数:"+transferCount+"耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime));
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
}
}



评论区